CARCINOMA AND SARCOMA: THE DIFFERENCE
Cancer is one of the deadliest diseases and kills people every now and then. The two most common types of cancer are: Carcinoma and Sarcoma. both of these cancers are malignant but still they have differences. Despite the numerous advancements in tumour and molecular biology over the past few years; the mortality rates due to cancer are very high. Carcinoma and Sarcoma are malignant forms of cancer but there are several differences between them, which one needs to know.
Carcinoma
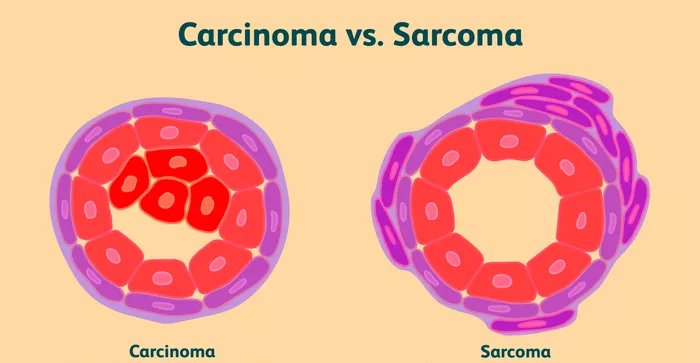
It is a malignant form which begins in the epithelial cells of the organs. There is an uncontrollable growth of epithelial cells in the inner or outer surfaces of the human body. This happens due to any alterations or damage caused in the DNA of a person and hence, results in disorderly growth of the cells. You should be aware of the fact that ‘not all cancers are carcinoma’.
Types of carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
It occurs in cell linings of organs, digestive tract or respiratory tract of the body. Mostly people associate squamous cell carcinoma with skin cancer, due to the fact that they show up on the skin. But it develops in the inner linings of the body too.
- Basal cell carcinoma
This is the most common type of cancer and develops in the cell lining of the outer layer of the skin.
- Invasive Ductal carcinoma
It is a form of breast cancer which grows in the ducts of breasts and gradually invades the fatty tissues of the breasts. It can also spread to the other parts of the body.
- Adenocarcinoma
This cancer occurs in “glandular cells” which means the cells which secrete mucus in the body. Adenocarcinoma can occur in the pancreas, lungs or colorectal region of the gut.
- Renal cell carcinoma
It is commonly called ‘kidney cancer’. It develops as a tumour in the cell linings of the kidney.
Causes
The underlying cause of this type of cancer could be mutation[i] in a cell. Mutation can lead to the damages in the DNA and ultimately cause abrupt growth of the cells. It is the process where cells grow continuously without any halt and disrupts the biochemical properties of other cells surrounding them. Certain combinations of mutations can also sabotage the DNA.
Sarcoma
It is the form of cancer which arises in the “mesenchymal cells” of the human body. They tend to grow in the connective tissues like bones, cartilage, blood vessels, fat and nerves of the body. Sarcoma is classified into two types and they have various subtypes based on the origin and type of a particular tissue from which the tumour arises.
Types of Sarcoma
- Soft tissue sarcoma
As the name signifies, this sarcoma originates in the soft tissues of the body, for instance, blood vessels, muscles, fat, lymph and nerves. They majorly arise in legs, arms and abdomen nevertheless they can grow anywhere in the body. There are multiple subtypes of soft tissue carcinoma like liposarcoma (adipose tissue), gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GI tract), leiomyosarcoma (smooth muscles) etc.
- Bone Sarcoma
These are uncommon forms of sarcoma and can develop anywhere in the bones but generally affects the long bones of legs and arms. Bone sarcoma could be benign or malignant. Chordoma (spinal cord), Chondrosarcoma (cartilage cancer) are some subtypes of bone sarcoma.
Causes
The causes of sarcoma are not well-known. Nevertheless, genetic mutations in the mesenchymal cells could be one of the possible reasons for this form of cancer. Exposure to some radiation could be a factor leading to sarcoma in the people.
We provide various primary cell lines for cancer research at Kosheeka, for further details contact us at info@kosheeka.com. Visit: www.kosheeka.com.
[i] https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/mutation