Primary Cells: Lifestyle Disease Models
Featured Products
- Wistar Rat Whole Blood
- Wistar Rat Serum
- Wistar Rat Plasma
- Wistar Rat Liver S9
- Wistar Rat Liver Microsomes
- Wistar Rat Liver Cytosol
- Wistar NK cells
- Wistar Mononuclear cells
- Wistar Mesenchymal stem cells
- Wistar Dermal fibroblasts
- Wistar Dendritic cells
- Villous Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Umbilical Cord Blood Derived Dendritic Cells
- Swiss Albino Mouse Lung S9
- Swiss Albino Mouse Liver S9
- Swiss Albino Mouse Liver Microsomes
- Swiss Albino Mouse Liver Cytosol
- Swine Skeletal Muscle Fibroblasts
- Swine Primary Bone Osteoblasts
- Swine Pancreatic Islets Cells
- Swine Lung Alveolar Cells
- Swine kidney Fibroblasts
- Swine Hepatocytes
- Swine Dermal Fibroblats
- Swine Cardiomyocytes
- Swine Cardiac Fibroblasts
- Swine Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cells
- Skin Dermal cells
- SD Rat Whole Blood
- SD Rat Serum
- SD Rat Plasma
- SD Rat Liver S9
- SD Rat Liver Microsomes
- SD Rat Liver Cytosol
- SD Rat Intestine S9
- SD Rat Intestine Cytosol
- SD Rat Intestinal Microsomes
- SD NK cells
- SD Muse cells
- SD Mononuclear cells
- SD Mesenchymal stem cells
- SD Dermal fibroblasts
- SD Dendritic cells
- Rhesus Monkey Whole Blood
- Rhesus Monkey Serum
- Rhesus Monkey Plasma
- Rat Schwann Cells Wistar
- Rat Schwann Cells SD
- Rat Schwann Cells Immuno-deficient
- Rat Pulmonary Fibroblasts Wistar
- Rat Pulmonary Fibroblasts SD
- Rat Pulmonary Fibroblasts Immuno-deficient
- Rat Lymphatic Fibroblasts Wistar
- Rat Lymphatic Fibroblasts SD
- Rat Lymphatic Fibroblasts Immuno-deficient
- Rat Hepatocytes Suspension Wistar
- Rat Hepatocytes Suspension SD
- Rat Hepatocytes Suspension Immuno-deficient
- Rat Hepatocytes Plateable-Wistar
- Rat Hepatocytes Plateable-SD
- Rat Hepatocytes Plateable-Immuno-deficient
- Rat Cardiomyocytes Wistar
- Rat Cardiomyocytes SD
- Rat Cardiomyocytes Immuno-deficient
- Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts Wistar
- Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts SD
- Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts Immuno-deficient
- Rat Brain Vascular Pericytes Wistar
- Rat Brain Vascular Pericytes SD
- Rat Brain Vascular Pericytes Immuno-deficient
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived NK Cells Wistar
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived NK Cells Immuno-deficient
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Muse Cells Wistar
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Muse Cells SD
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Muse Cells
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Mononuclear Cells Wistar
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Mononuclear Cells Immuno-deficient
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Mononuclear Cells
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Wistar
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells SD
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Immuno Deficient
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Dendritic Cells Wistar
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Dendritic Cells SD
- Rat Bone Marrow Derived Dendritic Cells Immuno-deficient
- Primary Hepatocytes Plateable C 57
- Primary Hepatocytes in Suspension CD-1
- Peripheral Blood-Derived Muse Cells
- Pancreatic islets beta cells
- Muse Cells
- Mouse Primary Bone Marrow Derived NK Cells CD1
- Mouse Primary Bone Marrow Derived NK Cells C57
- Mouse Muse cells CD1
- Mouse Muse cells C57
- Mouse Muse cells BalbC
- Mouse Hybrid Liver S9 Fraction Mixed Gender
- Mouse Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Mouse Derived Dendritic Cells
- Mouse DBA S9 Fraction Mixed Gender
- Mouse DBA Lung S9 Fraction Mixed Gender
- Mouse DBA Liver S9 Fraction Mixed Gender
- Mouse Cytosol Mixed Gender
- Mouse Cardiomyocytes C57
- Mouse Cardiomyocytes BalbC
- Mouse Cardiac Fibroblasts C57
- Mouse Cardiac Fibroblasts BalbC
- Mouse C57 BL/6N Liver S9 Fraction Mixed Gender
- Mouse Brain Vascular Pericytes
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Macaque Monkey blood mononuclear cells
- Lung alveolar cells
- Liver Hepatocytes plateable
- Lewis Rat Whole Blood
- Lewis Rat Serum
- Lewis Rat Plasma
- Kidney Fibroblasts
- Human Whole Blood
- Human Vaginal epithelial cells
- Human Umbilical Cord Blood Derived NK cells
- Human Umbilical Cord Blood Derived Mononuclear cells
- Human Umbilical Cord Blood Derived CD34+ Cells
- Human T Helper Cells
- Human Splenic Fibroblasts
- Human Splenic Endothelial Cells
- Human Skin S9 Fraction Mixed Gender
- Human Skin Derived Microvascular Dermal Endothelial Cells Adult
- Human Skin Derived Epidermal Melanocytes Fetal
- Human Skin Derived Epidermal Melanocytes Adult
- Human Skin Derived Epidermal Keratinocytes Neonatal
- Human Skin Derived Epidermal Keratinocytes Fetal
- Human Skin Derived Epidermal Keratinocytes Adult
- Human Skin Derived Dermal Fibroblasts Fetal
- Human Skin Derived Dermal fibroblasts Adult
- Human Skin Derived Dermal Fibroblasts Adult
- Human Seminal vesicles microvascular endothelial cells
- Human Seminal Vesicles Fibroblasts
- Human Seminal Vesicles Endothelial cells
- Human S9 Fraction Heart
- Human Pulmonary Small Airway Epithelial Cells
- Human Pulmonary Fibroblasts
- Human Pleatable Hepatocytes Pooled
- Human Plateable hepatocytes
- Human Peripheral Blood-Derived NK Cells
- Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Mononuclear Cells
- Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Monocytes
- Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Human Peripheral Blood-Derived Cytotoxic T-Cells
- Human Peripheral Blood Derived Serum
- Human Peripheral Blood Derived Plasma
- Human Pericardial Fibroblasts
- Human Ovarian Surface Epithelial Cells
- Human Ovarian Fibroblasts
- Human Muse cells
- Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Human Mast cells
- Human Mammary Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Mammary Fibroblasts
- Human Mammary epithelial cells
- Human Lung S9
- Human Lung Microsomes
- Human Lung Cytosol
- Human Liver S9
- Human Liver Microsomes
- Human Liver Cytosol
- Human Kidney Fibroblasts
- Human Islets Beta cells
- Human Islet Beta Cells
- Human Intestine S9
- Human Intestine Microsomes
- Human Intestine Cytosol
- Human Hepatocytes, Plateable
- Human Hepatocytes in Suspension
- Human Eye Derived Primary Retinocytes
- Human Eye Derived Limbal Fibroblasts
- Human Extra Embryonic Fetal Tissues Muse cells
- Human Extra Embryonic Fetal Tissues Derived CD34 Positive Cells
- Human Extra Embryonic Fetal Tissues Dendritic Cells
- Human Endometrial Epithelial Cells
- Human Cytotoxic T Cells
- Human Cord Blood Derived Serum
- Human cord blood derived Plasma
- Human Cardiomyocytes
- Human Cardiac Fibroblasts
- Human Bronchial Fibroblasts
- Human Bone Marrow-Derived NK Cells
- Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear cells
- Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Human Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic cells
- Human Bone Marrow-Derived CD 34 positive cells
- Human Bone Marrow Blood Derived Serum
- Human bone marrow blood derived Plasma
- Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells
- Human Aortic Endothelial Cells
- Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction
- Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Preadipocytes
- Human Adipose Tissue derived Mesenchymal Stem cells
- Horse peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- Horse mesenchymal stem cells-adipose tissue
- Hepatic Stellate Cells
- Golden Syrian Hamster Serum
- Golden Syrian Hamster Plasma
- Gingival Fibroblasts
- Endothelial cells
- Dog mesenchymal stem cells adipose tissue
- Dog hepatocytes plateable
- Dog blood mononuclear cells
- Dental Pulp Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Dendritic cells
- Cynomolgus Monkey Serum
- Cynomolgus Monkey Plasma
- Cynomolgus Monkey blood mononuclear cells
- Cynomolgus cryopreserved hepatocytes, plateable
- CD-1 Schwann cells
- CD-1 Pulmonary fibroblasts
- CD-1 NK cells
- CD-1 Muse cells
- CD-1 Mouse Whole Blood
- CD-1 Mouse Serum
- CD-1 Mouse Plasma
- CD-1 Mouse Lung S9
- CD-1 Mouse Lung Microsomes
- CD-1 Mouse Lung Cytosol
- CD-1 Mouse Liver S9
- CD-1 Mouse Liver Microsomes
- CD-1 Mouse Liver Cytosol
- CD-1 Mouse Intestine S9
- CD-1 Mouse Intestine Microsomes
- CD-1 Mouse Intestine Cytosol
- CD-1 Mononuclear cells
- CD-1 Mesenchymal stem cells
- CD-1 Hepatocytes plateable
- CD-1 Dermal Fibroblast
- CD-1 Dendritic cells
- CD-1 Cardiomyocytes
- CD-1 Cardiac fibroblasts
- CD-1 Brain vascular pericytes
- Cardiomyocytes
- Cardiac fibroblasts
- C57 Schwann cells
- C57 Pulmonary fibroblasts
- C57 NK cells
- C57 Muse cells
- C57 Mouse Whole Blood
- C57 Mouse Skin S9
- C57 Mouse Skin Microsomes
- C57 Mouse Skin Cytosol
- C57 Mouse Serum
- C57 Mouse Plasma
- C57 Mouse Lung S9
- C57 Mouse Lung Microsomes
- C57 Mouse Lung Cytosol
- C57 Mouse Liver S9
- C57 Mouse Liver Microsomes
- C57 Mouse Liver Cytosol
- C57 Mouse Intestine S9
- C57 Mouse Intestine Microsomes
- C57 Mouse Intestine Cytosol
- C57 Mouse Heart S9
- C57 Mouse Heart Microsomes
- C57 Mouse Heart Cytosol
- C57 Mononuclear cells
- C57 Mesenchymal stem cells
- C57 Hepatocytes Suspension
- C57 Dendritic cells
- C57 Cardiomyocytes
- C57 Cardiac fibroblasts
- C57 Brain vascular pericytes
- Brown Norway Rat Whole Blood
- Brown Norway Rat Serum
- Brown Norway Rat Plasma
- Beagle Whole Blood
- Beagle Serum
- Beagle Plasma
- Beagle Dog hepatocytes cryopreserved, plateable
- BalbC Schwann cells
- BalbC Pulmonary fibroblasts
- BalbC NK cells
- BalbC Muse cells
- BALBC Mouse Whole Blood
- BALBC Mouse Serum
- BALBC Mouse Plasma
- BalbC Mononuclear cells
- BalbC Mesenchymal stem cells
- BalbC Hepatocytes Suspension
- BalbC Hepatocytes plateable
- BalbC Dermal Fibroblasts
- BalbC Dendritic cells
- BalbC Cardiomyocytes
- BalbC Cardiac fibroblasts
- BalbC Brain vascular pericytes
- BALB/c Mouse Skin S9
- BALB/c Mouse Skin Microsomes
- BALB/c Mouse Skin Cytosol
- BALB/c Mouse Lung Cytosol
- BALB/C Mouse Liver S9
- BALB/c Mouse Liver Microsomes
- BALB/c Mouse Liver Cytosol
- BALB/c Mouse Intestine S9
- BALB/c Mouse Intestine Microsomes
- BALB/c Mouse Intestine Cytosol
- BALB/c Mouse Heart S9
- BALB/c Mouse Heart Microsomes
- BALB/c Mouse Heart Cytosol
- Amniotic Epithelial cells
Drop your Query
Primary cells, isolated from different donor tissues along with paired media for optimal cell growth and characterization are currently in demand, especially for pharmaceutical drug discovery efforts. These disease models are specifically designed to address various lifestyle diseases, including but not limited to autoimmune disorders, inflammatory disorders, skin injuries, etc. Some of these cellular disease models include cardiovascular disorders, lung disorders, arthritis, and diabetes.
With the availability of primary cells from specific tissue, it is now possible to understand the disease pathophysiology at the cellular and molecular levels. With the creation of relevant experimental models’ researchers are trying to mimic similar physiological conditions that are thought to be essential in developing new therapeutic modalities for chronic diseases. Additionally, disease models created using primary cells can be used for assessing clinical outcomes, and drug screening purposes.
Depending upon our client’s requirements, Kosheeka is happy to offer our unique range of primary cells that are customized as per demand. Choose from our wide range of inventory and start your experiments immediately.
Traditionally, research around the world was supported by cancer cell lines. These cell lines were the most preferred tools for all in vitro experimental studies, as well as the disease model of choice. Today, biomedical research has advanced crossing all the boundaries, with many impressive scientific accomplishments and a plethora of new insights into disease mechanisms. While these advancements have certainly helped the scientific community to bring forth new treatment modalities, they also outline the persistent challenges as well as limitations that are being faced in translational research; such as the use of inadequate disease models due to the unavailability of specific cell lines, cell line contamination as well as cell line misidentification. These issues are further complicating the risky, costly, and time-consuming nature of drug screening.
With the major leap in the era of translational medicine, the biomedical field is getting equipped with reliable resources for faster and more affordable personalized treatments. In the race against primary cells and the use of immortalized cell lines, the latter is largely reconsidered.
Accordingly, Kosheeka has supported the creation of different ‘disease models’ created using our wide portfolio. The disease models created using a single type of primary cells are helpful in better understanding due to the reduction in complexity of the disease; hence, these models have become easy to explore. With the easy availability of primary cells and the ability to produce them on a mass scale, we can provide cells to you as per your requirements.
Accordingly, some of the extensively used primary cells for creating different disease models are:
- Primary Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells for Lung Disorders
- Primary Human Skin fibroblasts for Wound healing
- Primary Human Cardiomyocytes for Cardiovascular Disorders
- Primary Human lung Fibroblasts for Asthma
- Primary Human Preadipocytes for Diabetes Type II
- Primary Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem cells for Diabetes Type II
- Complete growth medium for optimum growth and maintenance.
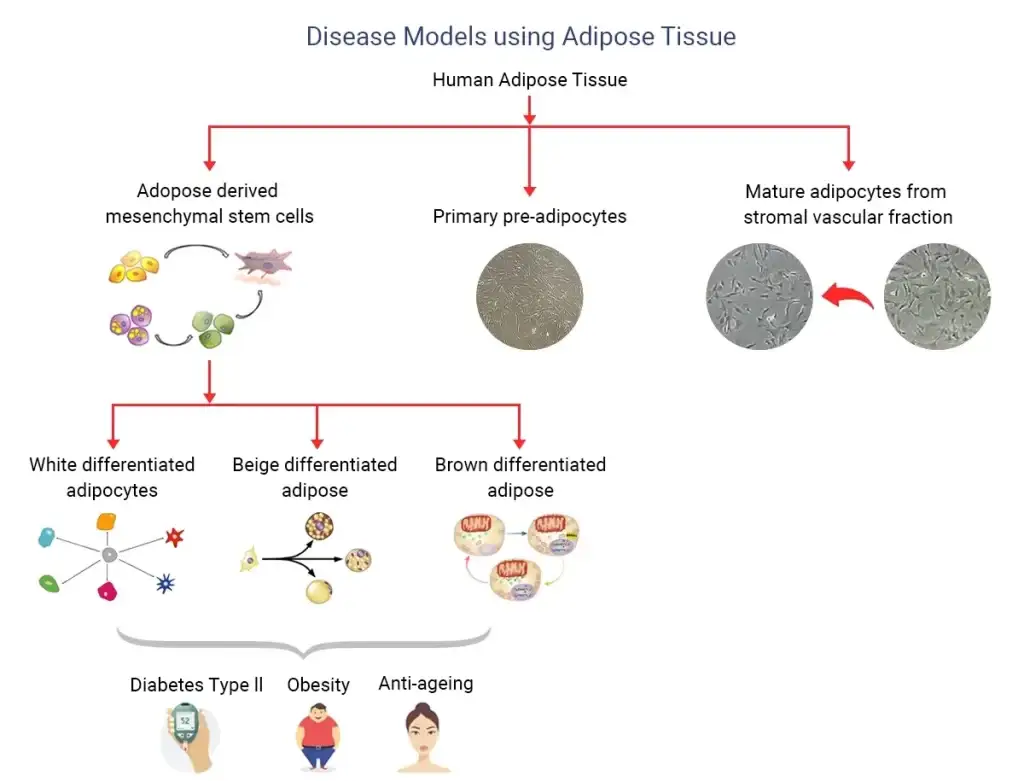
Diabetes Type II Disease Model
All of us are aware of the growing incidences of obesity, causing higher mortality due to important pathological consequences, like Diabetes Type II. With current statistical analysis, by 2030; developed countries like America would be handling approximately 350 million individuals with more attribution of expenditure, estimated to be around 132 million $ in the US alone.
Studies have indicated that progressive deterioration of adipogenic potential of preadipocytes, present in adult human bodies may importantly contribute to the adipose tissue dysfunction leading to obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Various studies are also proposing variable epigenomic signatures as well as transcriptomic responses at the cellular level to be responsible for the differentiation pattern; hence, in vitro disease models were developed using primary human preadipocytes to study transcriptome profiles, epigenetic signatures sourced from lean, obese and obese with Type 2 Diabetes patients.
Asthma Cellular Disease Model
Similarly, in disease models like asthma research and drug development; various primary cells from bronchial, and tracheal tissues of human origin are commonly used. This can also be a way out to avoid regulatory obligations in case of animal usage. The models created with the help of primary cells are still considered benchmarks; despite them being high in cost, difficult to be available, and difficult to maintain in culture for a longer period. Whereas, various freshly isolated primary cells from bronchial or airway tissues like human bronchial epithelial cells, etc. under appropriate culture conditions, may get differentiated into pseudostratified monolayers of mixed epithelial cells, further being considered as the best possible in vitro representation of bronchial epithelium, as confirmed by some of the studies.
Some of the common primary cells, used as a disease model in respiratory illnesses including Asthma are
- Primary Human Aortic Endothelial Cells
- Primary Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells
- Primary Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells
- Primary Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells
- Primary Human Carotid Artery Endothelial Cells
- Primary Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- Primary Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells
